The Secrets of Successfully Upskilling and Reskilling Your People
- Upskilling and reskilling are key concerns in organizations today, made more important by the advent of AI
- But very few know how to do it, and many companies struggle with it
- The process can be made more successful with appropriate personalisation for individual learners and job roles, but few know how to achieve that either.
- Martec's Upskilling and Reskilling Blueprint will tell you how to plan it and manage its execution to a successful steady state conclusion with a quantified return on investment.
- Our examples will focus on retailing and consumer goods because that’s Martec’s core competence. But you can use this model in any industry.
- Our goal is that when you need someone in a role, you have people ready to be promoted because they have been developed for the role already.
Part 1 The Blueprint
Martec International has developed an Upskilling and Reskilling Blueprint to address how you and your company can do this successfully. The blueprint has three main phases:
- Provisioning everthing you need to launch a successful project.
- Building a quantified plan.
- Executing the plan.
The blueprint kit includes:
- Three approximately 20-minute videos giving a detailed overview of the methodology.
- A range of templates to use during provisioning, planning and implementation
- A time-based spreadsheet based planning model which can be used for pilot projects or complete company upskilling projects
- A spreadsheet based comprehensive return on investment model which can be used initially to estimate the investment cost and the return on investment in the project. Subsequently, it can be used in the execution phase to check that the benefits are being achieved, or to identify any gaps and rectify them.
- An e-learning return on investment class to help those not too familiar with comprehensive return on investment modelling.
- A detailed written guide to the methodology to help step you through the project. This document includes guidance on to how to incorporate personalisation both for the company and individual learners.
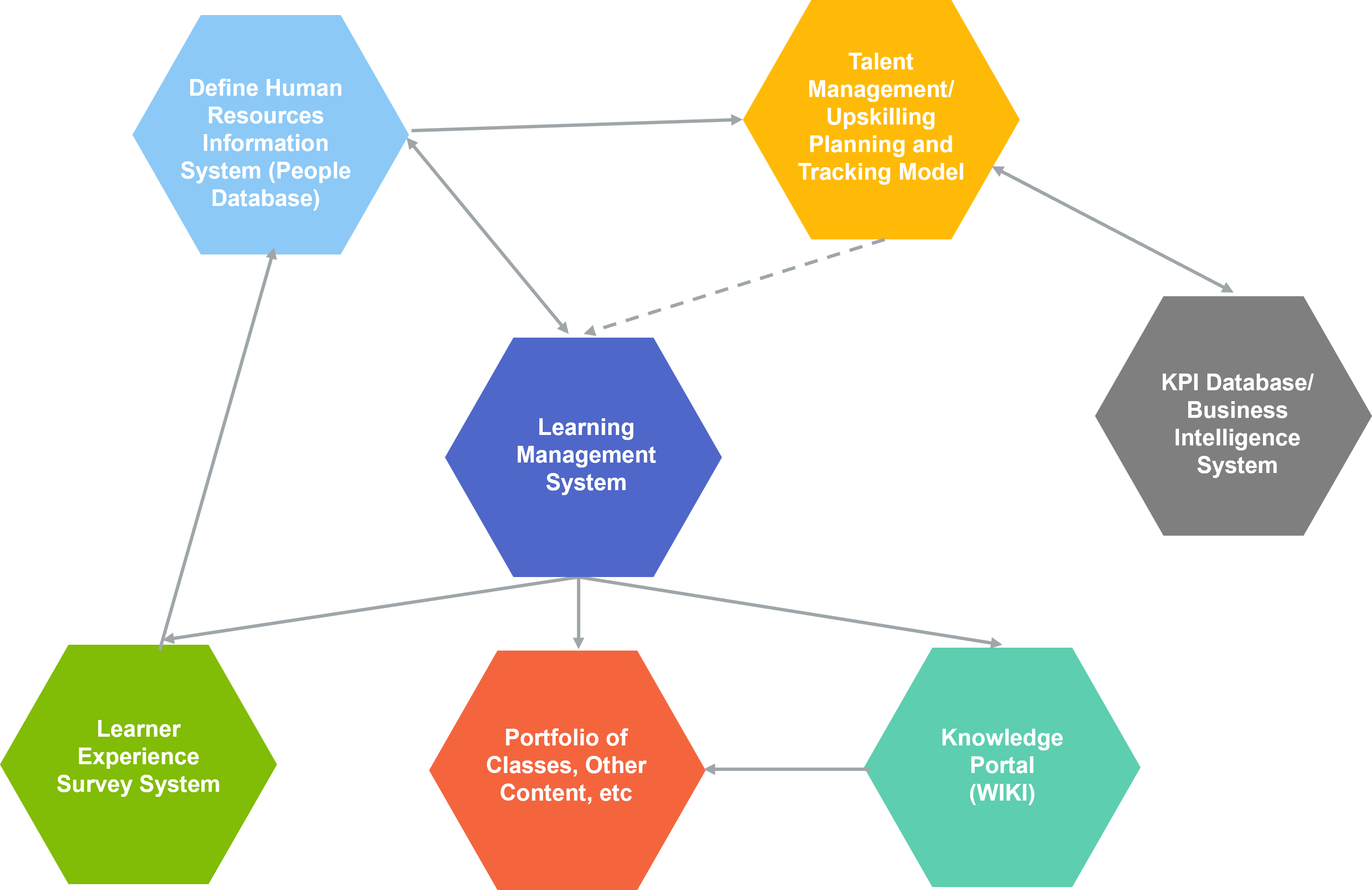
In addition to the blueprint, Martec can supply a complete portfolio of classes and other learning interventions, plus optional learning management software. We do not supply "horizontal" training classes, such as leadership development, critical thinking skills, etc., but many suppliers do and Martec is happy to work with them to achieve the right result. This becomes potentially important in the personalisation for the company concerned.
Most providers of learning solutions and company L&D departments struggle with demonstrating the return on investment for projects of this nature. Martec is happy to demonstrate its approach. This is based on many years of consulting experience, which involved developing ROI models for much more expensive projects such as implementing SAP Retail and Microsoft Dynamics retail solutions.
One aspect of our approach is that we have a one to one mapping between each job role and its associated learning path. (More about this later). For example, in the case of store merchandisers, the selected KPIs might include % availability on store shelves and the weeks cover held in each store for a specifc department, depending on what the company's systems can support. These KPIs can be estimated initially if no history exists and then tracked through implementation. Department by department, you can review the change in average inventory over time and see whether it is achieving the planned reduction. If not, the level of granularity in the ROI model allows forensic analysis of the data to see where the problem is and what needs to be addressed.
Overview of Upskilling Process

Part 2 Background
The project can start with a small scale pilot project to learn the best lessons, or perhaps start with one department like Buying and Merchandising and then roll out to other departments as required. Either way, the description of our process that follows will cover it.
The first step is to either review an existing career path map and edit it if necessary, or build one to serve as the starting point. Here's an example:

Each job role on the career map should have a job description and that should help define the competencies needed to be considered as proficient in that role. Martec can supply a list of competencies for each job role addressing the retail specific processes that need to be included. The L&D team can add competencies to that list for horizontal skills, such as critical thinking and spreadsheet mastery.
Then a learning path is designed to teach the skills and comptencies for that list of requirements. Martec can supply it's learning paths, which cover all normal retail or consumer goods company requirememts, and clients can add their own sections for horizontal skills.
Martec learning paths contain a variety of learning interventions as explained on the home page. A key point to note is that Martec learning paths include key performance indicators that should be tracked to assess how well that learning path is working and to feed into our ROI model. Not all job roles will have associated KPIs but a lot will.
At this point, if this is a pilot project, you can procure any additional resources you need to conduct the pilot, like training classes you do not already have. You can see our guidance in the diagram below.
Part 3 Planning
The next step is to populate the plannning model template included in our blueprint.

You could do this one year at a time with monthly columns for the year, or use the same template but define the columns as quarterly and cover the forward three years. An annual example is shown above. Full details of how to complete this and all charts are given in the detailed blueprint explanation. The model formulae will need to change for each functional area included.
The main purpose of the model is to plan how many people you will need in reach role to allow for a variety of factors, such as new store openings, store closings, shutdowns for refurbishment, different rates of attrition, etc. This section is developed on the Creating The Initial Plan Chart.

As far as headcount is concerned you will arrive at two numbers in each month, how many existing people need to be ready for promotion to that job role in each month and how many external recruits will need to be on board and inducted by then.
The bottom part of this chart is where the training hours needed are calculated.
For a significant project, you can then use this data together with the return on investment model in the kit to produce an estimated cost of the upskilling and the projected return on investment..
When the first pass of the plan is complete, you can examine the forecasted training hours and cost needed using a 9-box or 16-box model and see whether you need to adjust some of the risk/reward ratios in the learning paths to bias the cost allocation to where you think it will do the most good.
Completing these charts assumes that you have completed the learning path chart shown below.

For now, the important things to note on this chart are the KPIs assigned to each job role and the risk/reward ratio. You can use the risk/reward ratio and the estimated training costs in conjunction with the 9-Box analysis, to help you prioritise where to focus the allocation of potential budget to get the best return on the investment. This will help you set the priorities for a pilot project or the inital priority areas to focus on.
Omce the project is approved you can commence implementation. Before you do that though, it would be a good idea to plan how you will support change management as you go through implementation.
Part 4 Implementation
Implementation involves getting everyone started on their individual learning paths. For a pilot, you could ignore personalisation, but for a bigger initial phase you might well want to include it.
The chart below shows how implementation is tracked. The bulk of the training in this example is Martec classes. But Deputy Store Managers have two assignments that have to be completed too. Name 2 in the table has a series of classes allocated but none have been started yet. Name 1 has completed one class and passed the mastery test. He or she has also been given a credit pass on leadership skills because they are deemed to have demonstrated that competency already, by one of various means (see Blueprint for details). They have also been given credit for their store level inventory management ability by demonstrating the competency in their current role. His or her original workplan of 30 hours is now down to 25 hours as a result of these factors.
This tracking provides the means to check that there will be enough deputy store managers ready for promotion in time to meet the plan needs, or to assess where additional action needs to be taken to accelerate progress towards the goal.
![]()
![]()
The ability to do the business performance tracking will depend in part on information being accessible from your IT systems.
In this example the first KPI tracked for potential store managers is how the store sales performance is changing over time. In this case figures are captured at the end of each month (EOM). It will take some time for performance to improve noticeably, so the best comparison is probaly sales against plan. After several months are you starting to see the improvement over plan levels increasing? As we go into the first half of the next year, we can do a season on season comparison, assess the percentage growth and compare it to the forecast in the initial ROI analaysis and see whether it is on track. If not, the way our ROI model is built, we can identify whether the performance is not being achieved because of traffic issues, in-store conversion rates, achieved average transaction size in money and units, the level of returns or combinations of these factors. We can then investigate the detail, review the training and follow up support and determine what needs to be done to rectify this situation.
This process can then be applied to all the KPIs for all the included job roles. Where necessary, the ROI model can be re-run in the light of the outturn to re-forecast the results as necessary.
Part 5 More Information
This page is a summary of highlights of the upskilling and reskilling process. Full details are given in the upskilling and reskilling blueprint document, which forms a valuable imput to planning such a project.
There are also three 20-minute videos which describe the process in detail. If upskilling and/or reskilling is on your agenda, we will happily provide access to these, so you can assess our contribution to this type of project.
The blueprint touches on things that we have not included in this summary, which will become important in future, such as the potential impact of AI on the development of businesses in general. For example, if AI does eliminate more entry level jobs, how will you ensure that enough candidates move through the career development stages, so that you have enough skilled people to manage a plethora of AI agents and identify when they are producing incorrect results? How do you get enough skilled candidates to be developed as warehouse shift managers, if there aren't a number of suitable people being identified for development from those in more junior positions?
For an initial discussion discussion on your potential needs, or to request access to the video series, please click this link and to register your need and we will respond promptly.
